Today you will learn how to use different numeral systems in the Scalar calculator. Thanks to Scalar it is very easy to:
- Convert decimal system to other numeral systems
- Convert other numeral systems into a decimal system
- Enter values simultaneously in different numeral systems
- Acquire information about the digits of a given number on the basis of the indicated numeral system
Stay tuned, this is exciting 🙂
⭐ Conversion to other numeral systems
Conversion of the number to different numeral systems is done at the end, i.e. after determining the value of the expression. User indicates in which numeral system the result should be presented. General syntax:
<NumeralSystem> expression
- binary: bin expression
- octal: oct expression
- decimal: expression
- hexadecimal: hex expression
- base-n: base.n expression
Please follow the below examples
Scalar code result:
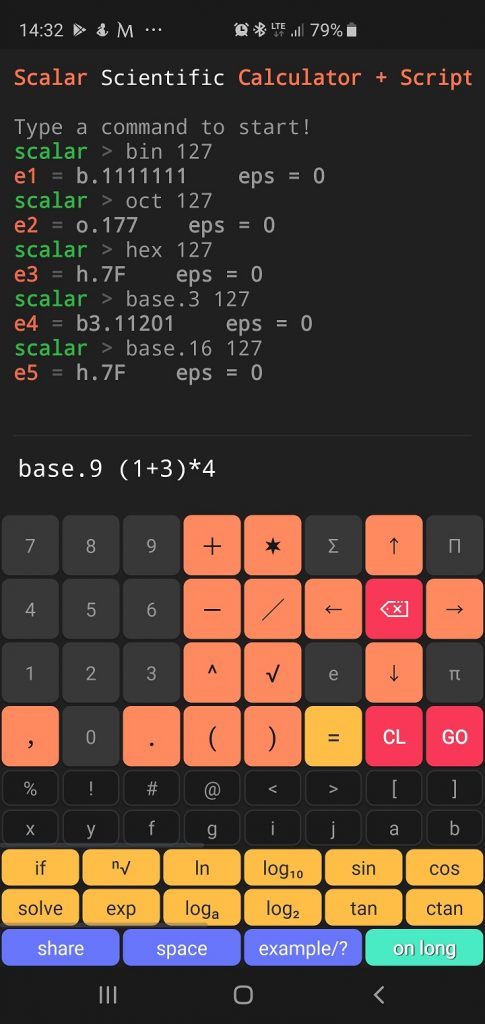
scalar > bin 127 e1 = b.1111111 eps = 0 scalar > oct 127 e2 = o.177 eps = 0 scalar > hex 127 e3 = h.7F eps = 0 scalar > base.3 127 e4 = b3.11201 eps = 0 scalar > base.16 127 e5 = h.7F eps = 0 scalar > base.9 (1+3)*4 e6 = b9.17 eps = 0
Scalar script:
bin 127 oct 127 hex 127 base.3 127 base.16 127 base.9 (1+3)*4
⭐ Convert to decimal system
The mathematical engine of Scalar always works in one numeral system, so before it is possible to determine the result of an expression, all values given in different numeral systems are converted to one decimal standard. In Scalar you can enter numbers using any numeral system. General syntax:
<NumericalSystemPrefix.>NumberLiteral
- binary: b.XXXX
- octal: o.XXXX
- decimal: XXXX
- hexadecimal: h.XXXX
- base-n: b<n>.XXXX
Please follow the below examples
Scalar code result:
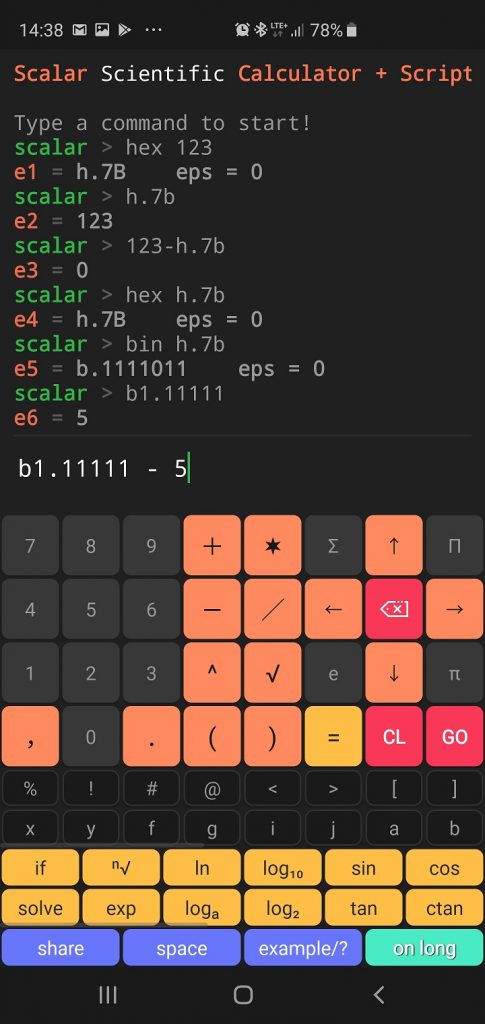
scalar > hex 123 e1 = h.7B eps = 0 scalar > h.7b e2 = 123 scalar > 123-h.7b e3 = 0 scalar > hex h.7b e4 = h.7B eps = 0 scalar > bin h.7b e5 = b.1111011 eps = 0 scalar > b1.11111 e6 = 5 scalar > b1.11111 - 5 e7 = 0
Scalar script:
hex 123 h.7b 123-h.7b hex h.7b bin h.7b b1.11111 b1.11111 - 5
⭐ Mixing different numeral systems in a single expression
Scalar is very flexible, thus there is no limitation in terms of entering number in various numeral systems.
Scalar code result:
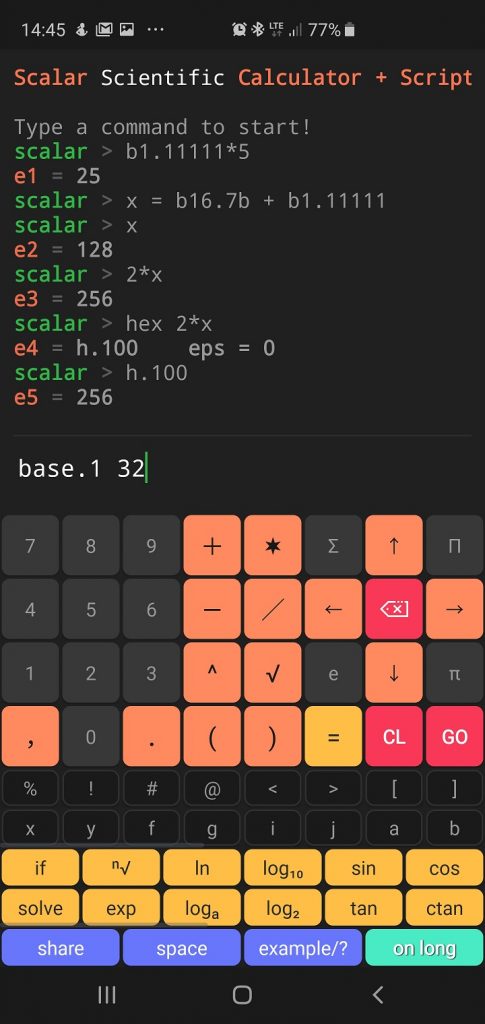
scalar > b1.11111*5 e1 = 25 scalar > x = b16.7b + b1.11111 scalar > x e2 = 128 scalar > 2*x e3 = 256 scalar > hex 2*x e4 = h.100 eps = 0 scalar > h.100 e5 = 256 scalar > base.1 32 e6 = b1.11111111111111111111111111111111 eps = 0
Scalar script:
b1.11111*5 x = b16.7b + b1.11111 x 2*x hex 2*x h.100 base.1 32
⭐ Numerical systems with higher base
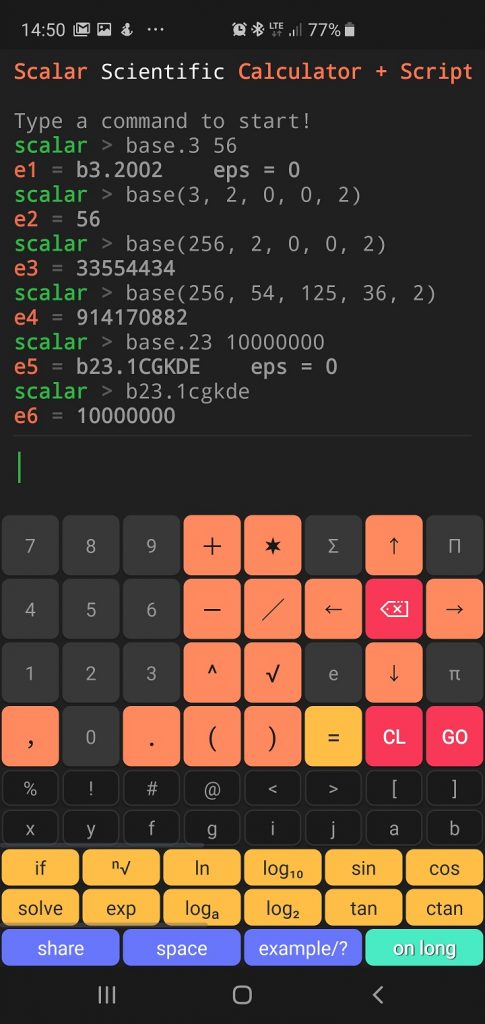
Using a standard alphabet, i.e. alphabetical order of letters, you can enter numbers in a numeral system with base between 1 and 36. In case of any larger bases, please use the function base (n, …) that accepts many parameters.
Scalar code result:
scalar > base.3 56 e1 = b3.2002 eps = 0 scalar > base(3, 2, 0, 0, 2) e2 = 56 scalar > base(256, 2, 0, 0, 2) e3 = 33554434 scalar > base(256, 54, 125, 36, 2) e4 = 914170882 scalar > base.23 10000000 e5 = b23.1CGKDE eps = 0 scalar > b23.1cgkde e6 = 10000000
Scalar script:
base.3 56 base(3, 2, 0, 0, 2) base(256, 2, 0, 0, 2) base(256, 54, 125, 36, 2) base.23 10000000 b23.1cgkde
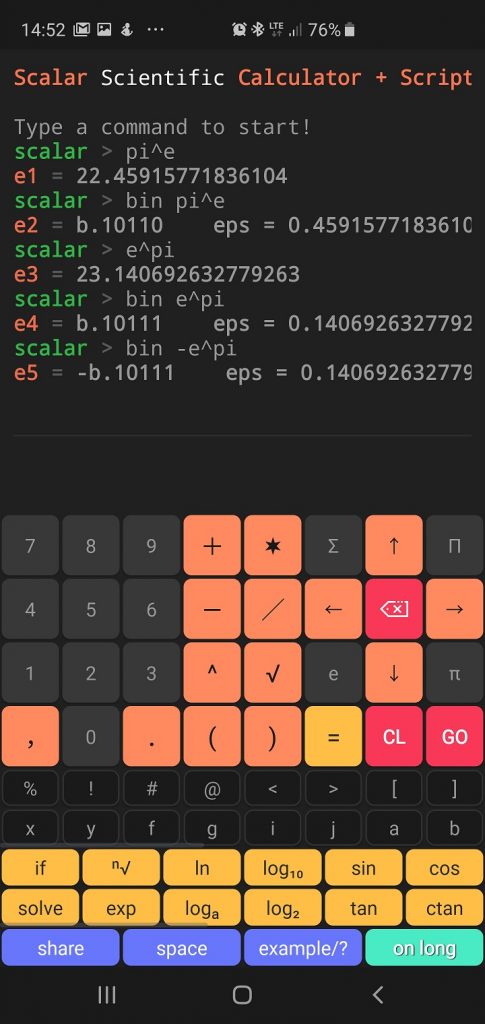
⭐ Non integers conversion
During the conversion of the result to the indicated numeral system, only the integer part is converted. Please follow the epsilon remark to be sure what part was not converted.
Scalar code result:
scalar > pi^e e1 = 22.45915771836104 scalar > bin pi^e e2 = b.10110 eps = 0.45915771836104113 scalar > e^pi e3 = 23.140692632779263 scalar > bin e^pi e4 = b.10111 eps = 0.14069263277926325 scalar > bin -e^pi e5 = -b.10111 eps = 0.14069263277926325
Scalar script:
pi^e bin pi^e e^pi bin e^pi bin -e^pi
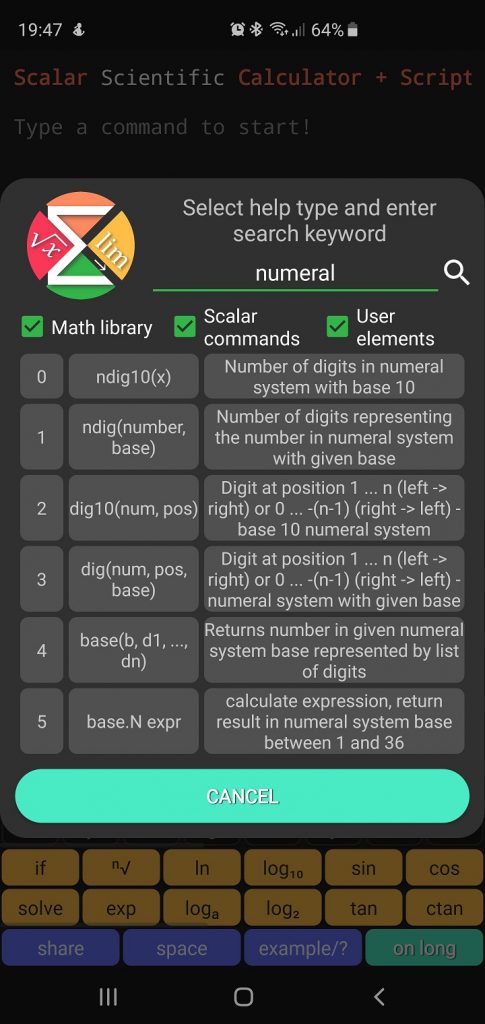
⭐ Acquiring information about digits
Scalar provides several clever functions that allow to obtain information about the digits of a given number. Long press the “example /?” button and enter “numeral” in the search field. You will be presented with the list of functions.
- ndig10(x) – number of digits of a number in base 10
- ndig(x, base) – number of digits of a number in any base
- dig10(x, position) – digit of a number in base 10 at specified position
- dig(x, position, base) – digit of a number in any base at specified position
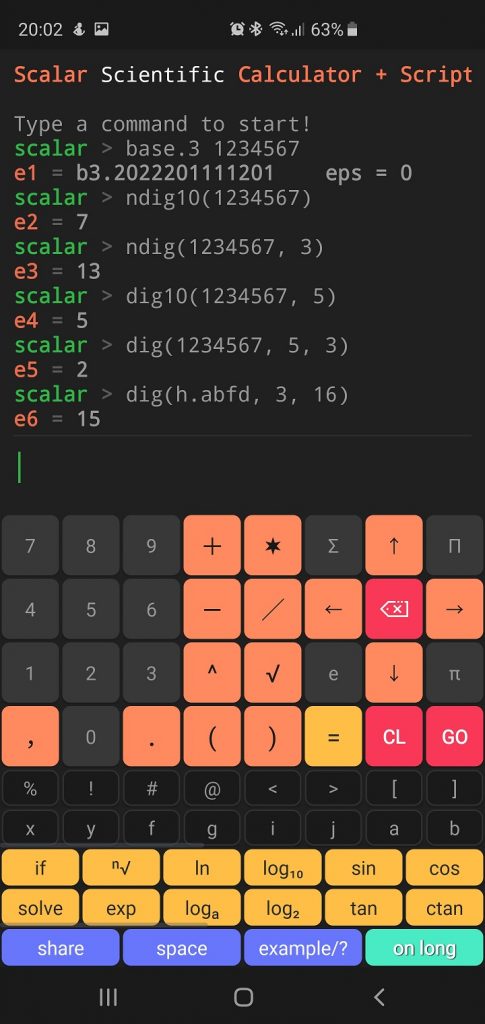
And a few examples:
Scalar code result:
scalar > base.3 1234567 e1 = b3.2022201111201 eps = 0 scalar > ndig10(1234567) e2 = 7 scalar > ndig(1234567, 3) e3 = 13 scalar > dig10(1234567, 5) e4 = 5 scalar > dig(1234567, 5, 3) e5 = 2 scalar > dig(h.abfd, 3, 16) e6 = 15
Scalar script:
base.3 1234567 ndig10(1234567) ndig(1234567, 3) dig10(1234567, 5) dig(1234567, 5, 3) dig(h.abfd, 3, 16)
? Thank you 🙂
Thank you for reading and thank you for using Scalar. If you like my app please make me a gift posting a review on Google Play store.
? Scalar in action
? Scalar Free

? Scalar Pro

Best regards